Data come from the 1991 Arizona cardiovascular patient files. A subset of the fields was selected to model the differential length of stay for patients entering the hospital to receive one of two standard cardiovascular procedures: CABG and PTCA. CABG is the standard acronym for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft, where the flow of blood in a diseased or blocked coronary artery or vein has been grafted to bypass the diseased sections. PTCA, or Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty, is a method of placing a balloon in a blocked coronary artery to open it to blood flow. It is a much less severe method of treatment for those having coronary blockage, with a corresponding reduction in risk.
Below we show a snapshot of the data set:
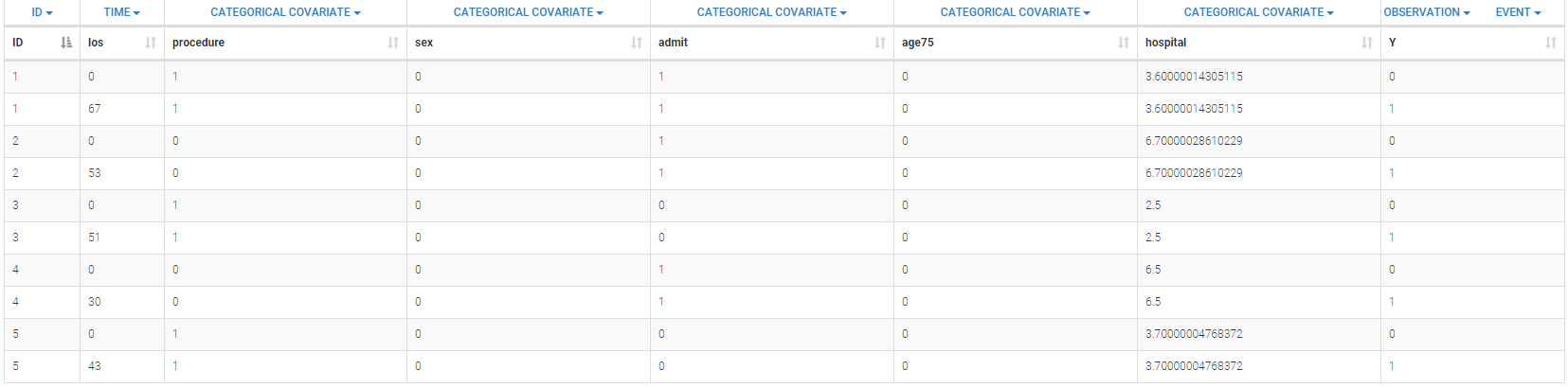
The definition of the columns is the following:
- ID: patient identifier, column-type ID
- los: time in days when the patient goes out of the hospital, column-type TIME
- procedure: procedure used, 1 or 0 (1 for CABG and 0 for PTCA), column-type CATEGORICAL COVARIATE
- sex: sex of the patient, 1 or 0 (1 for Male and 0 for female), column-type CATEGORICAL COVARIATE
- admit: type of admission, 1 or 0 (1 for Urgent/Emergency and 0 for elective), column-type CATEGORICAL COVARIATE
- age75: is the subject’s age over 75 years, column-type CATEGORICAL COVARIATE
- hospital: string describing the hospital, column-type CATEGORICAL COVARIATE
- Y: event type (0 to enter in the hospital, 1 when the event ‘The subject leaves the hospital’ happens), column-type OBSERVATION
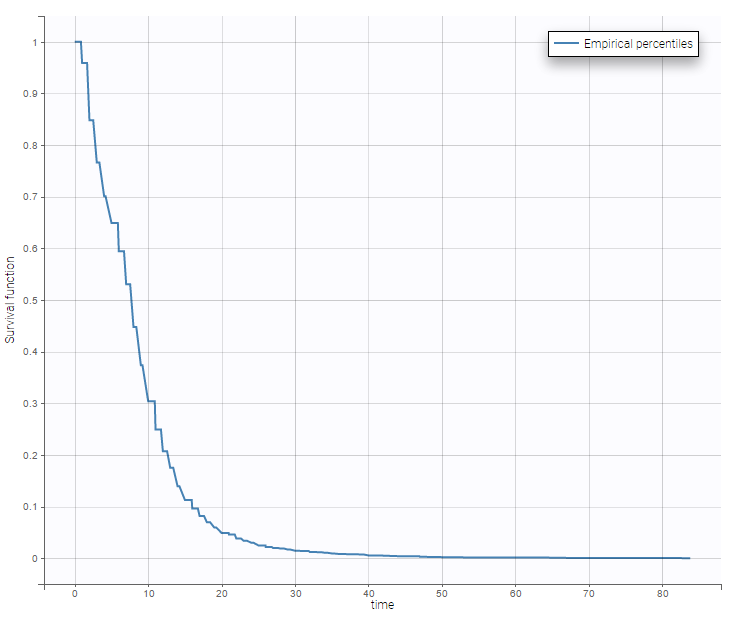
The representation of the Keiplan-Meier curve with respect to time is presenter below.